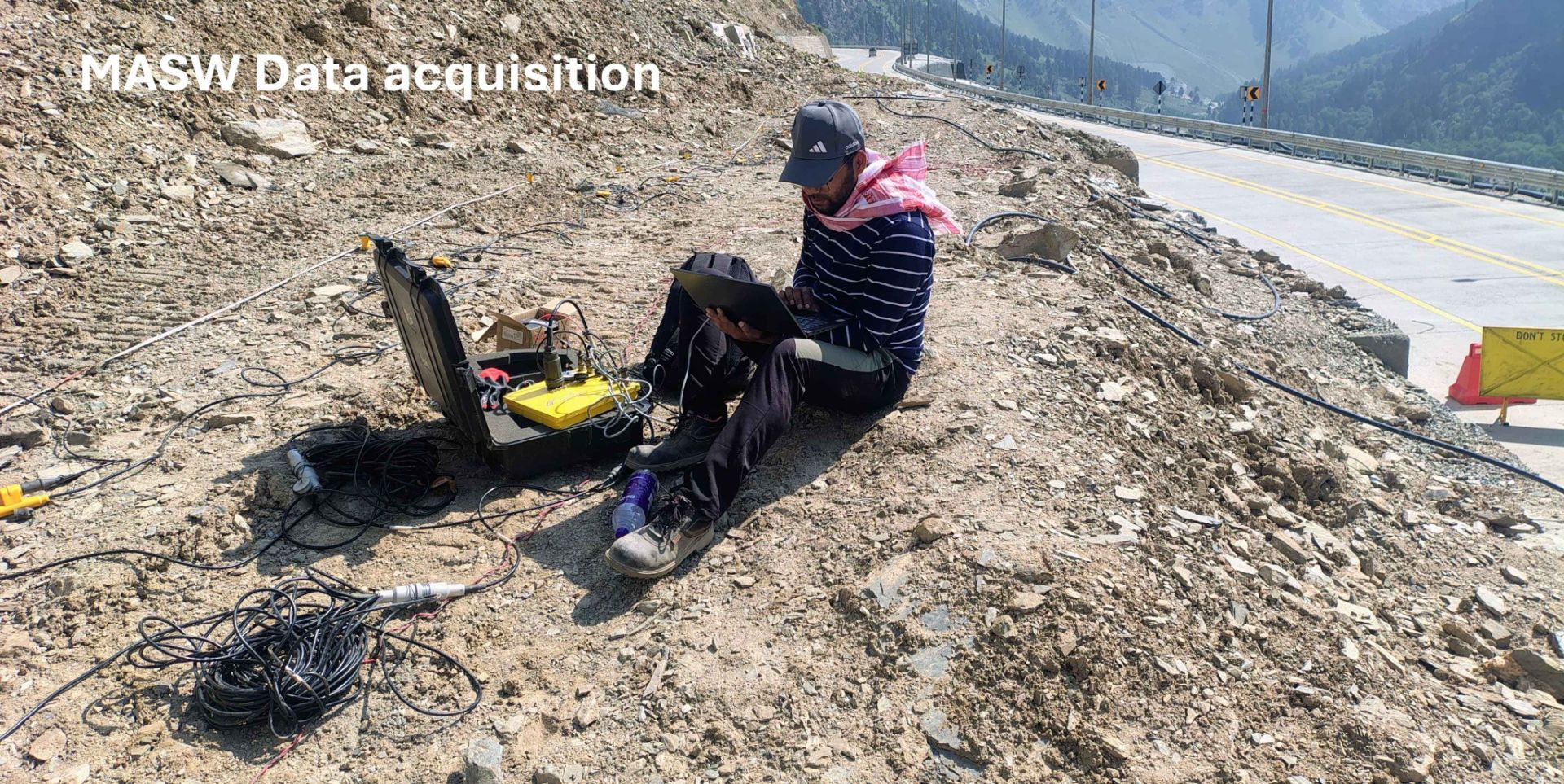
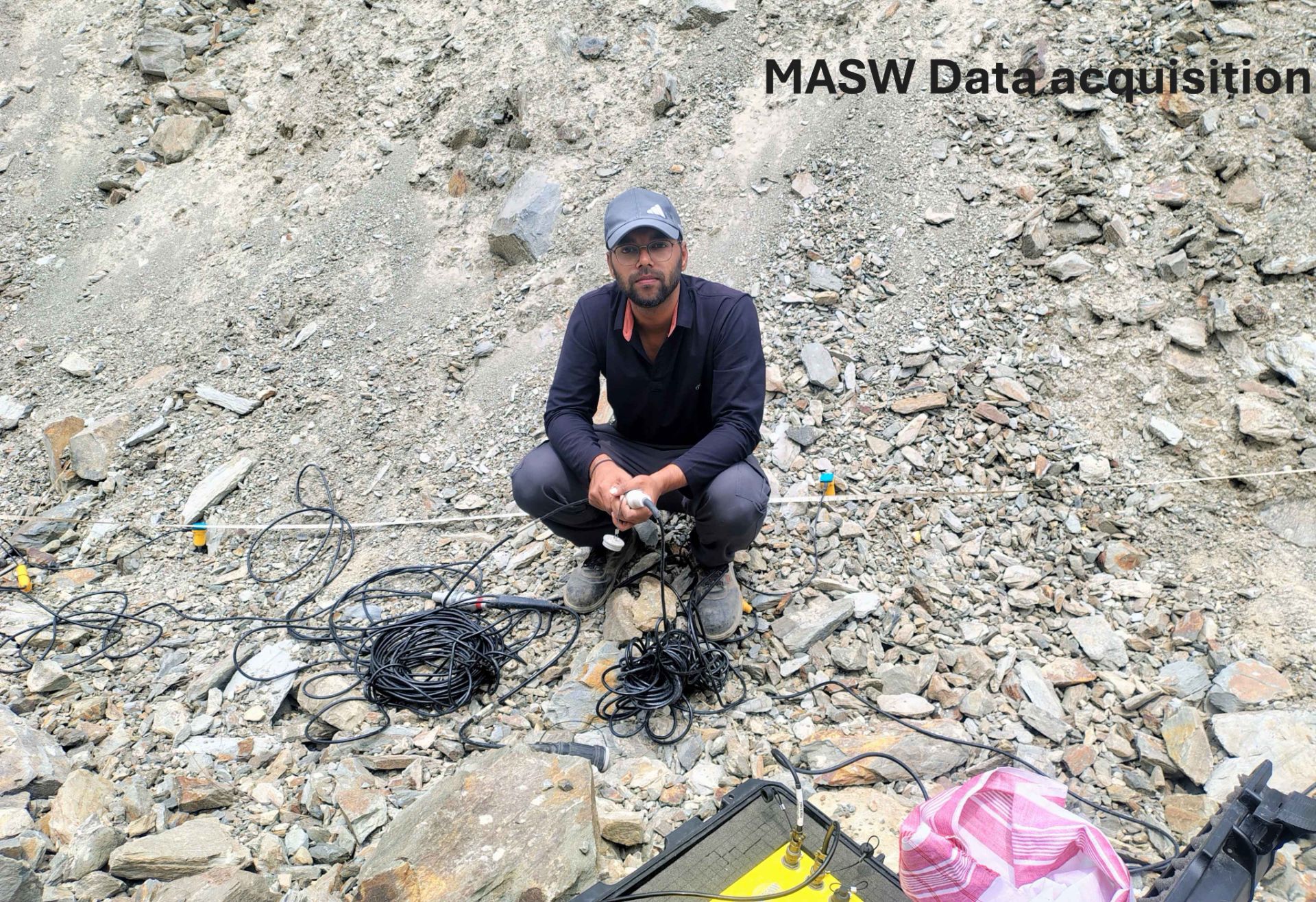
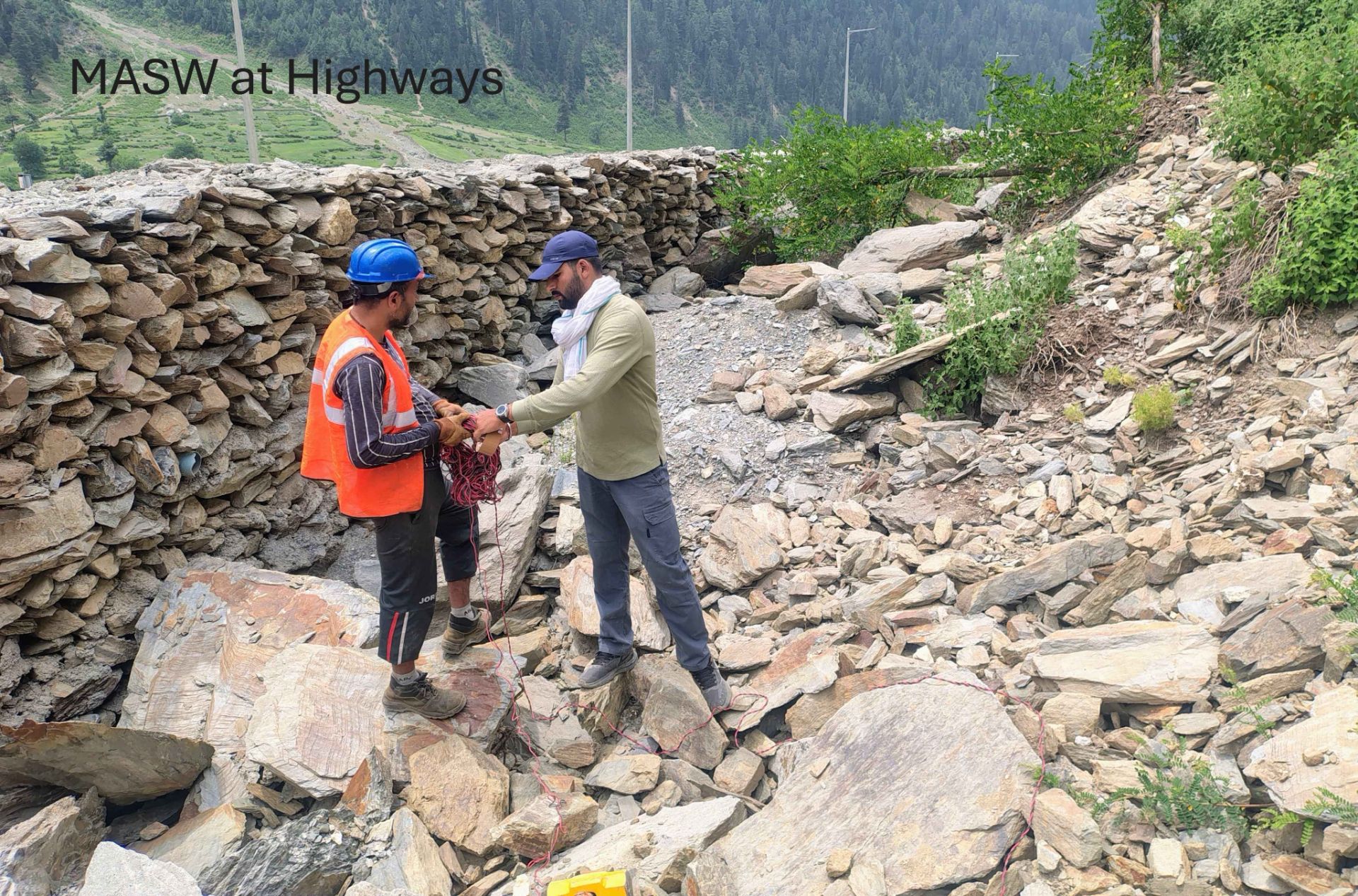
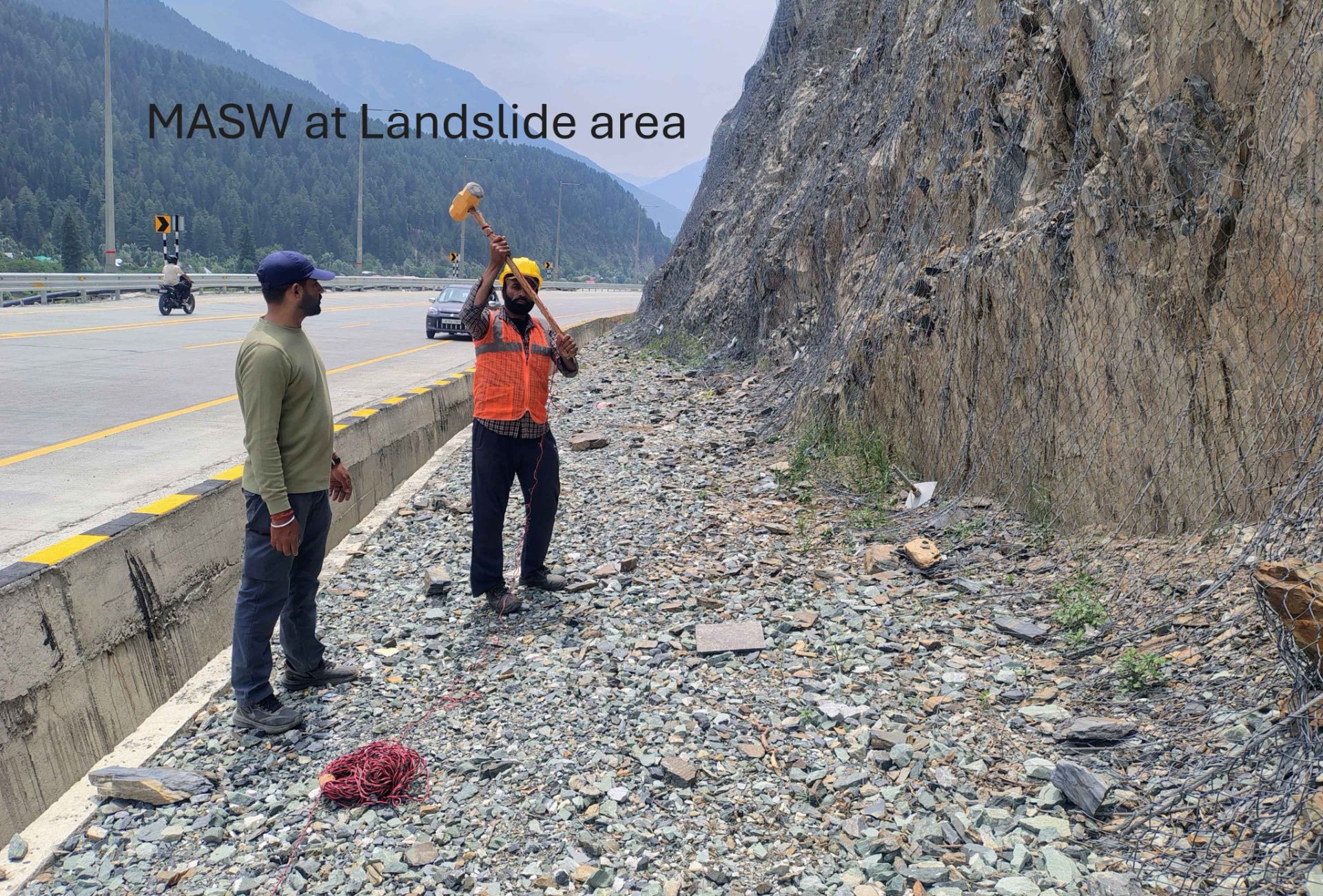
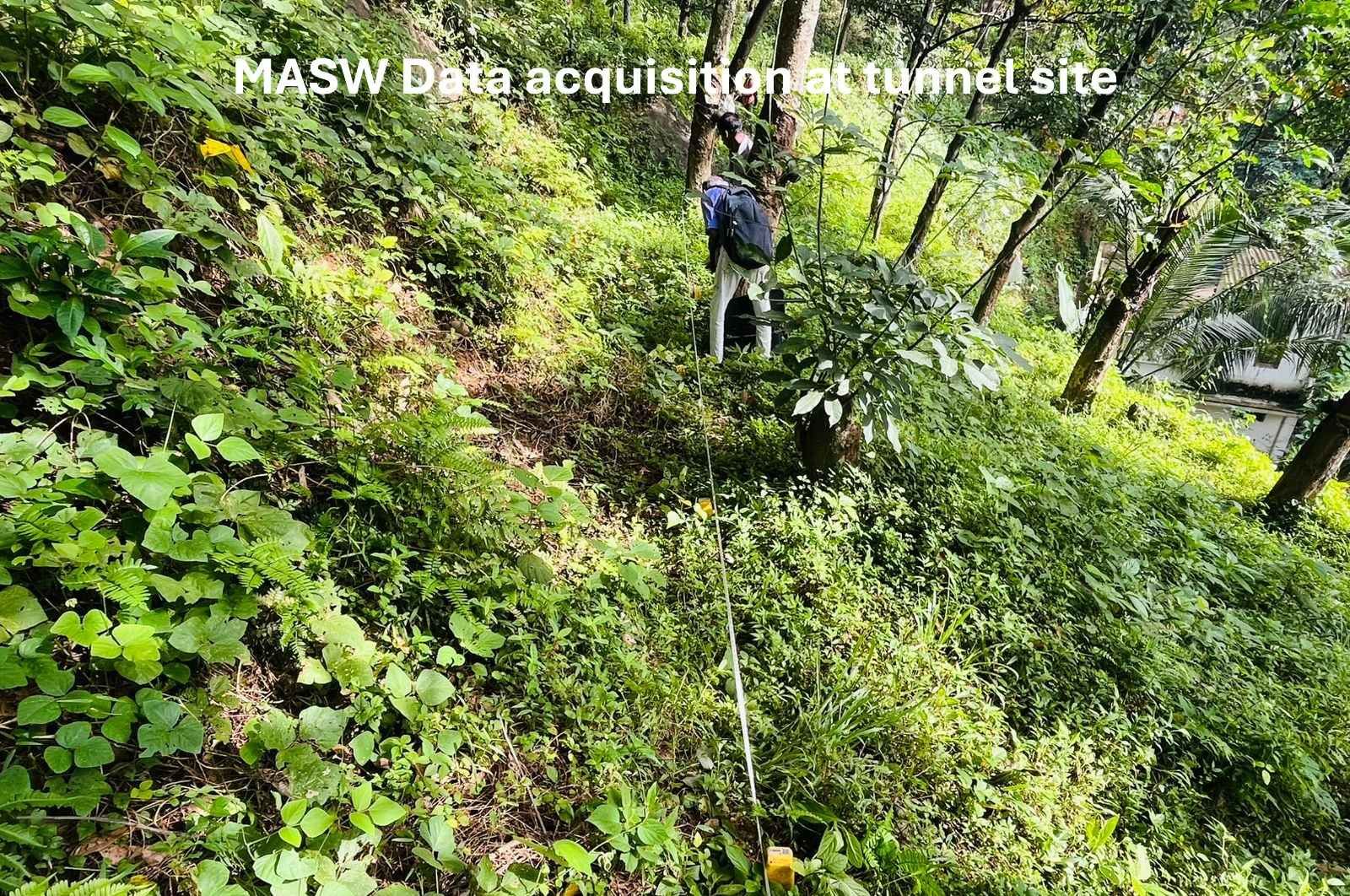
Multi Channel Analysis of Surface Waves
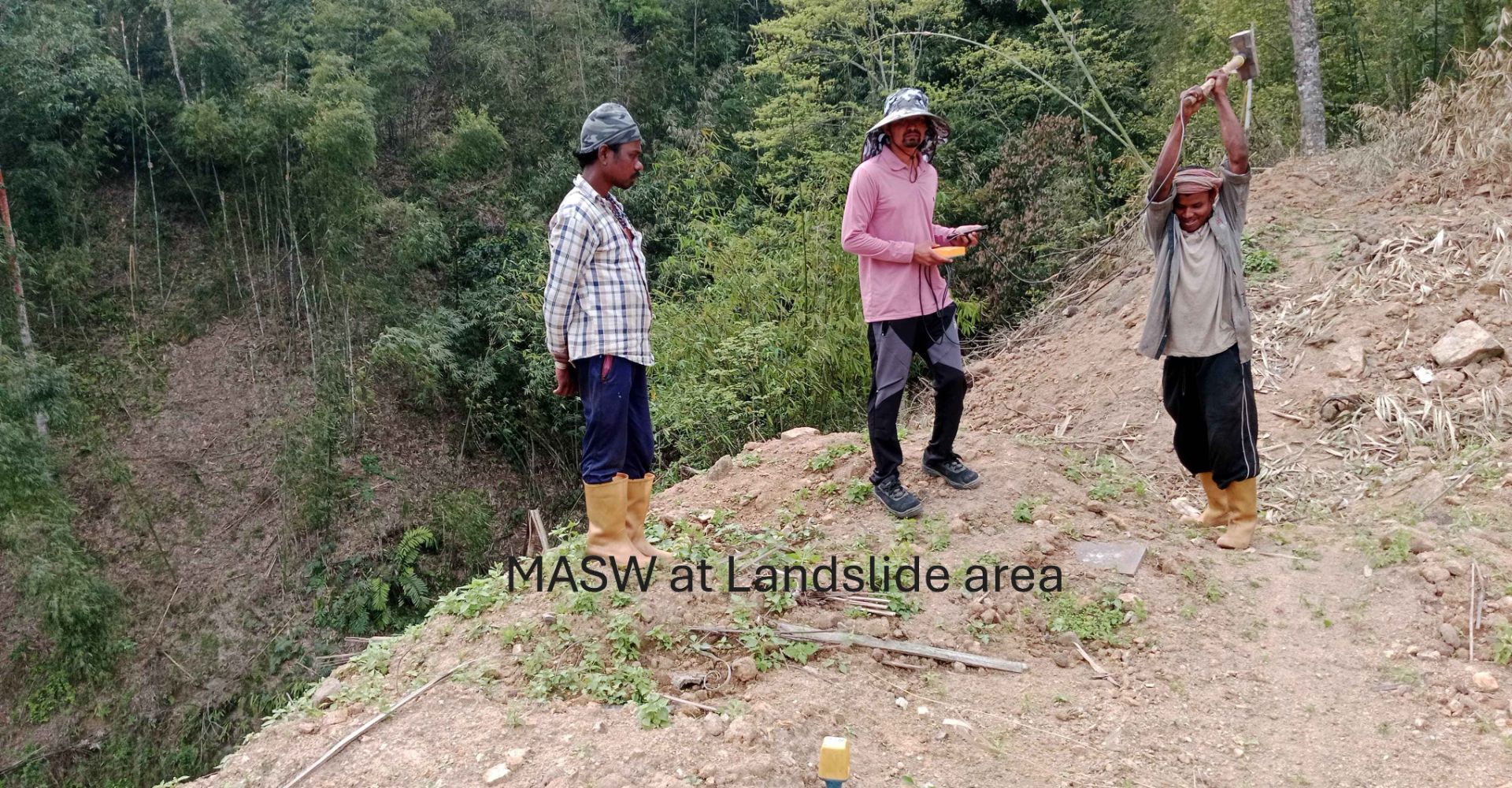
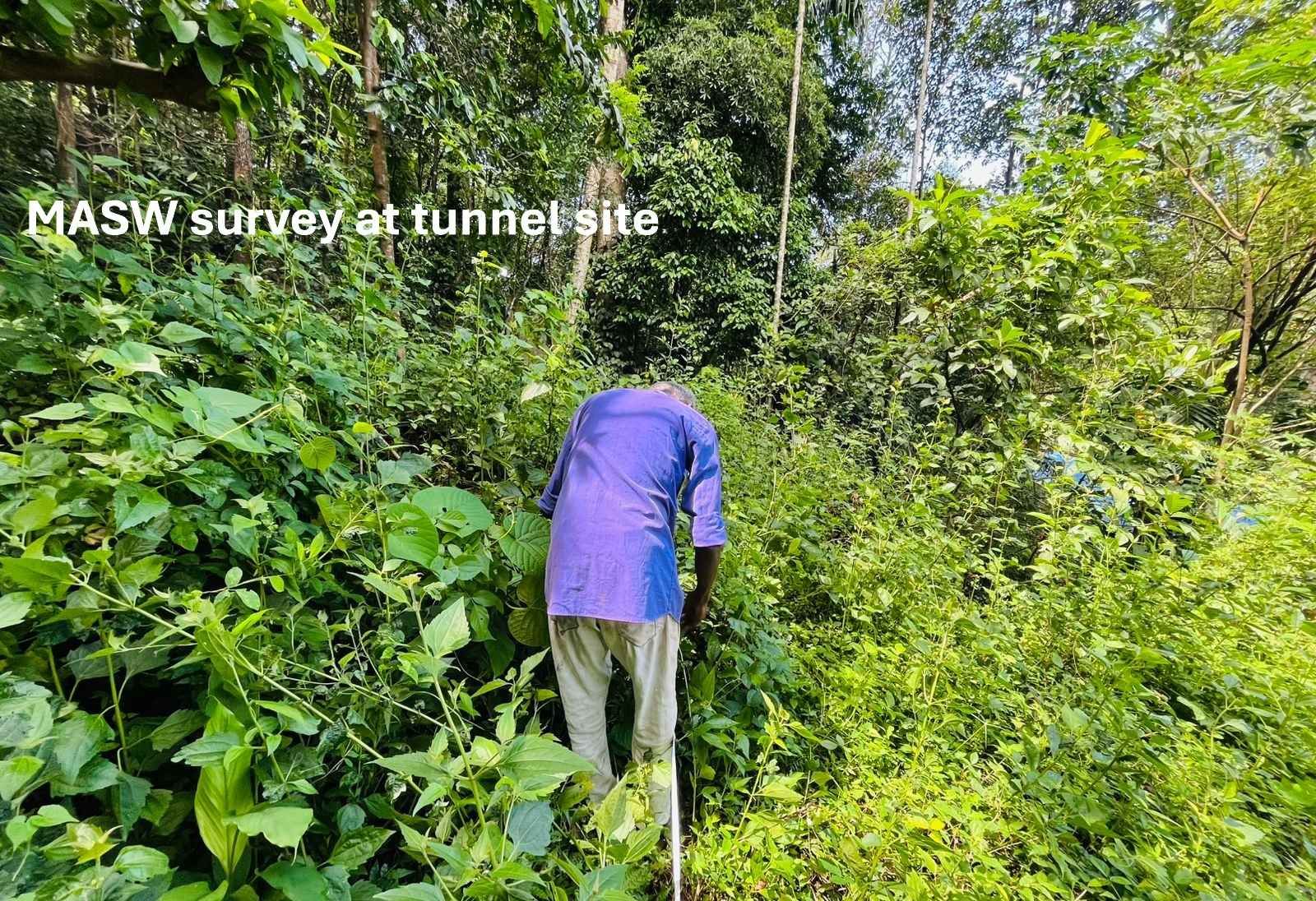
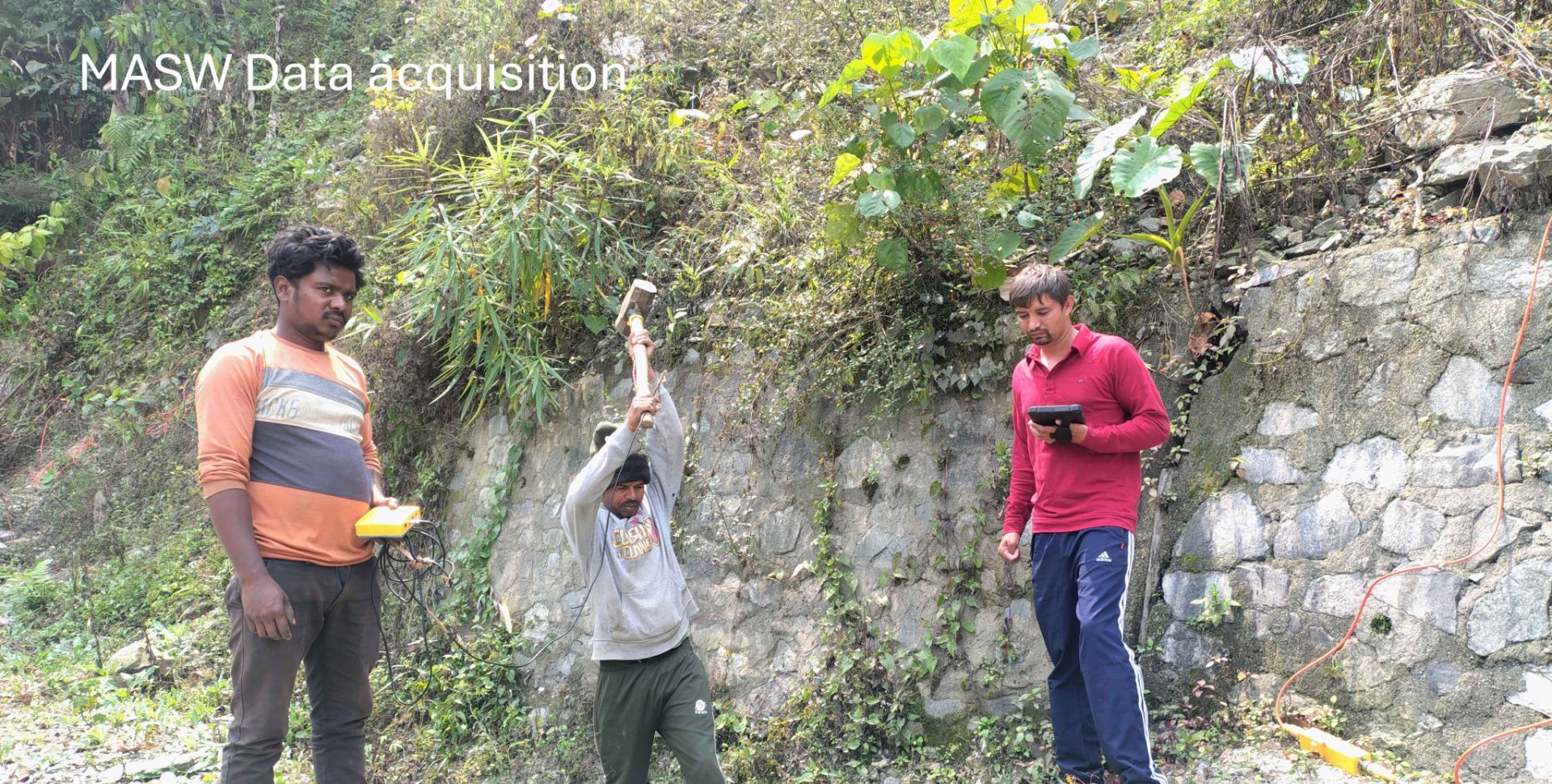
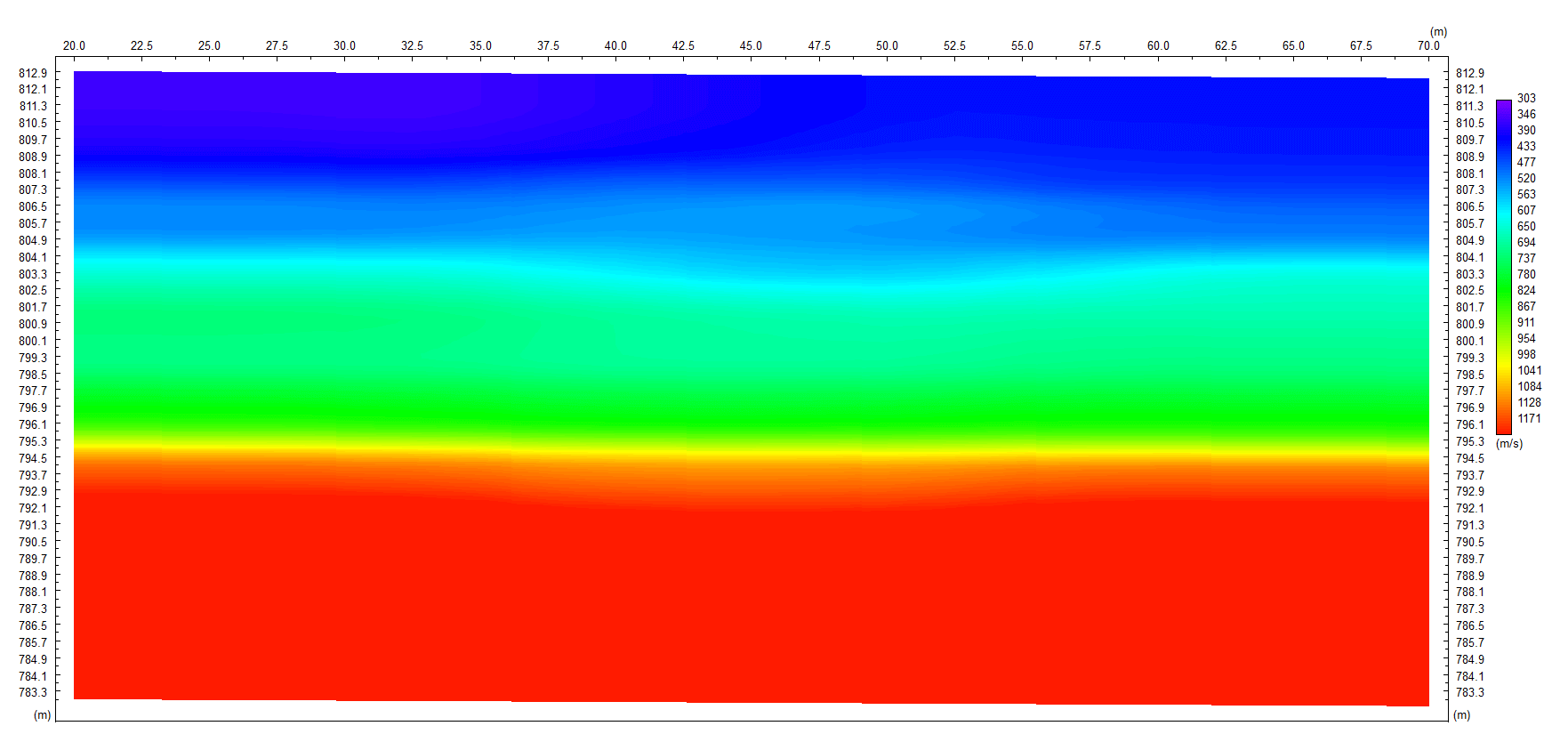
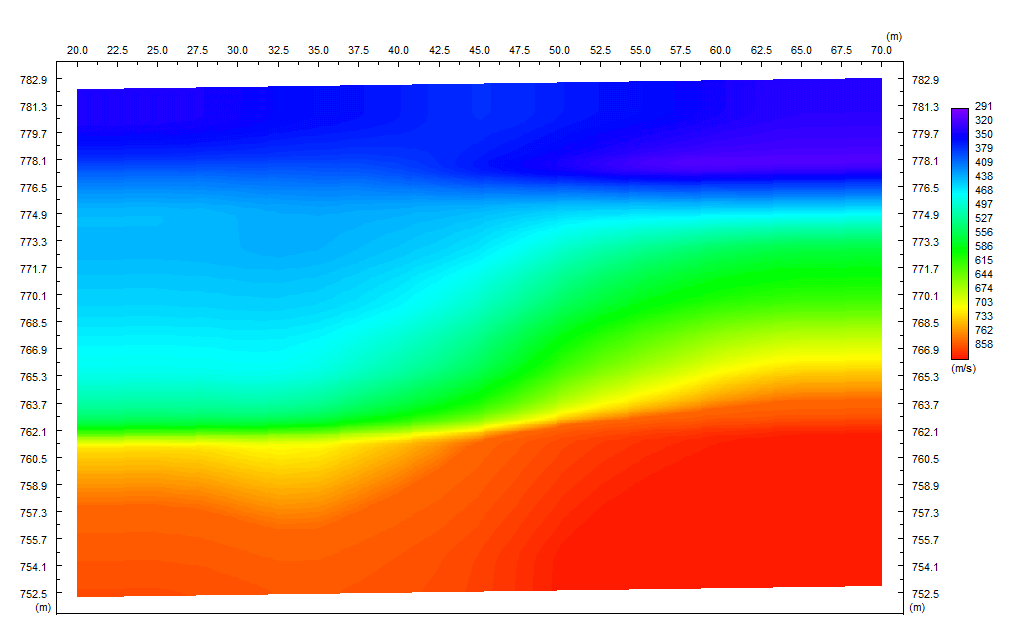
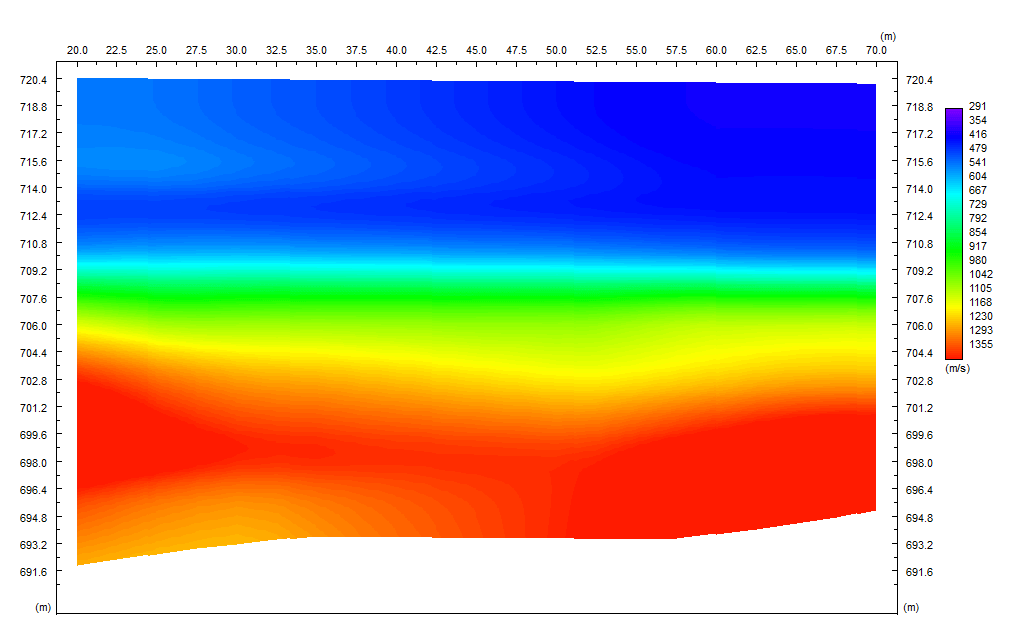
Multichannel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW) surveying is an active and passive method based on the measurement of Shear Wave Velocity (Vs) which is an indicator of the ground stiffness. Surface waves allow the measurement of the variation in small strain ground stiffness (Gmax) with depth.The surface wave technique is based upon the dispersion or change in phase velocity with frequency of a seismic wave propagating through the subsurface. Longer wavelengths penetrate to deeper depths whilst shorter wavelengths are sensitive to the elastic properties of shallower layers. Surface wave dispersion is significant in the presence of velocity layering, which is common in the near-surface environment. Although there are other types of surface waves, the term "surface wave" when used in the SASW (Spectral Analysis of Surface Waves), MASW (Multi-channel Analysis of Surface Waves), or MAM (Microtremor Array Measurement) context has come to mean the Rayleigh wave. Since the Rayleigh wave is the dominant component of ground roll, it is also referred to as "ground roll". There is no difference in the Rayleigh waves generated by different systems, but the method used to generate and record the waves differs.

Applications of Multichannel Analysis Of Surface waves
- Stratigraphic mapping and depth to bedrock
- Anomaly detection (e.g., voids and tunnels)
- Characterization of poorly consolidated or weak ground
- Soil stiffness and ground improvement verification
- Assessment of engineering properties of soil/rock mass
- Seismic hazard analysis
- Ground stiffness mapping
- Detection of subsurface anomalies
- Assessment of liquefaction potential
- Pavement evaluation
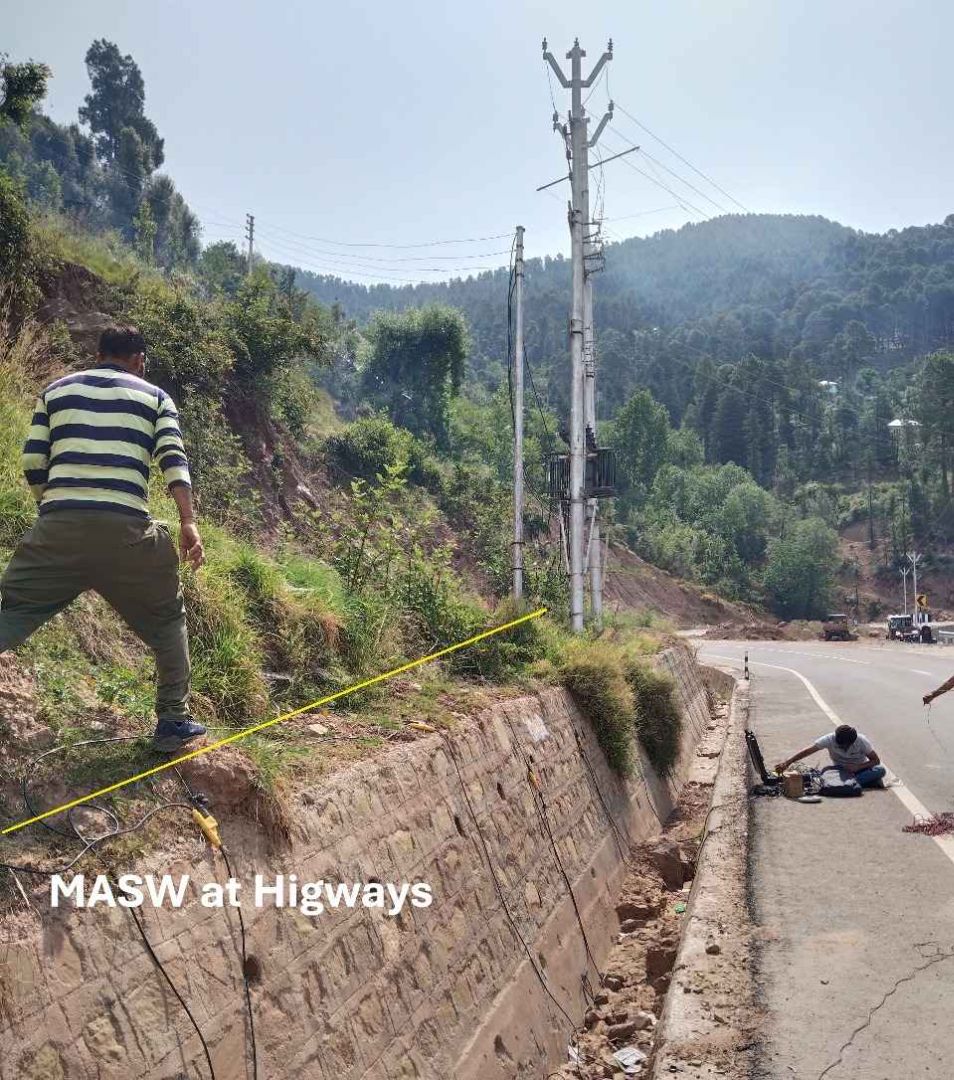
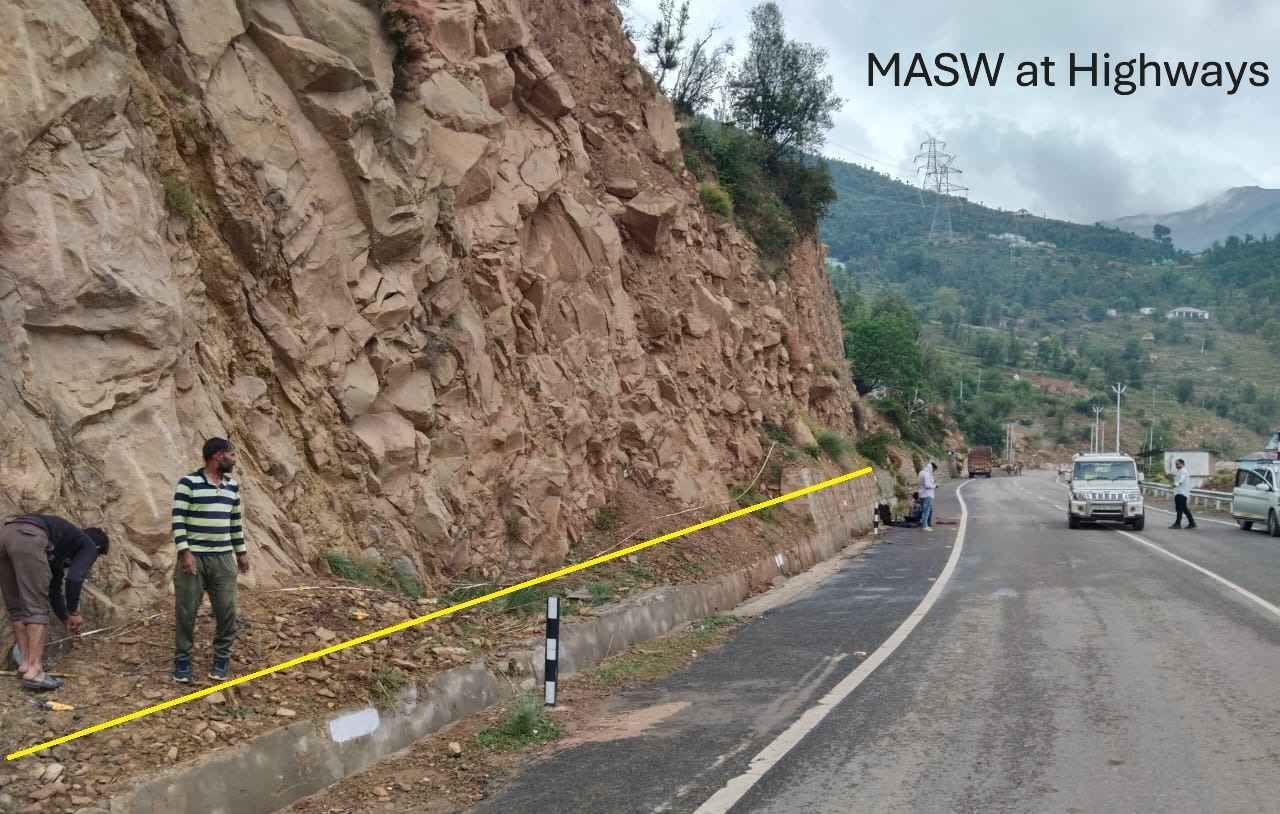
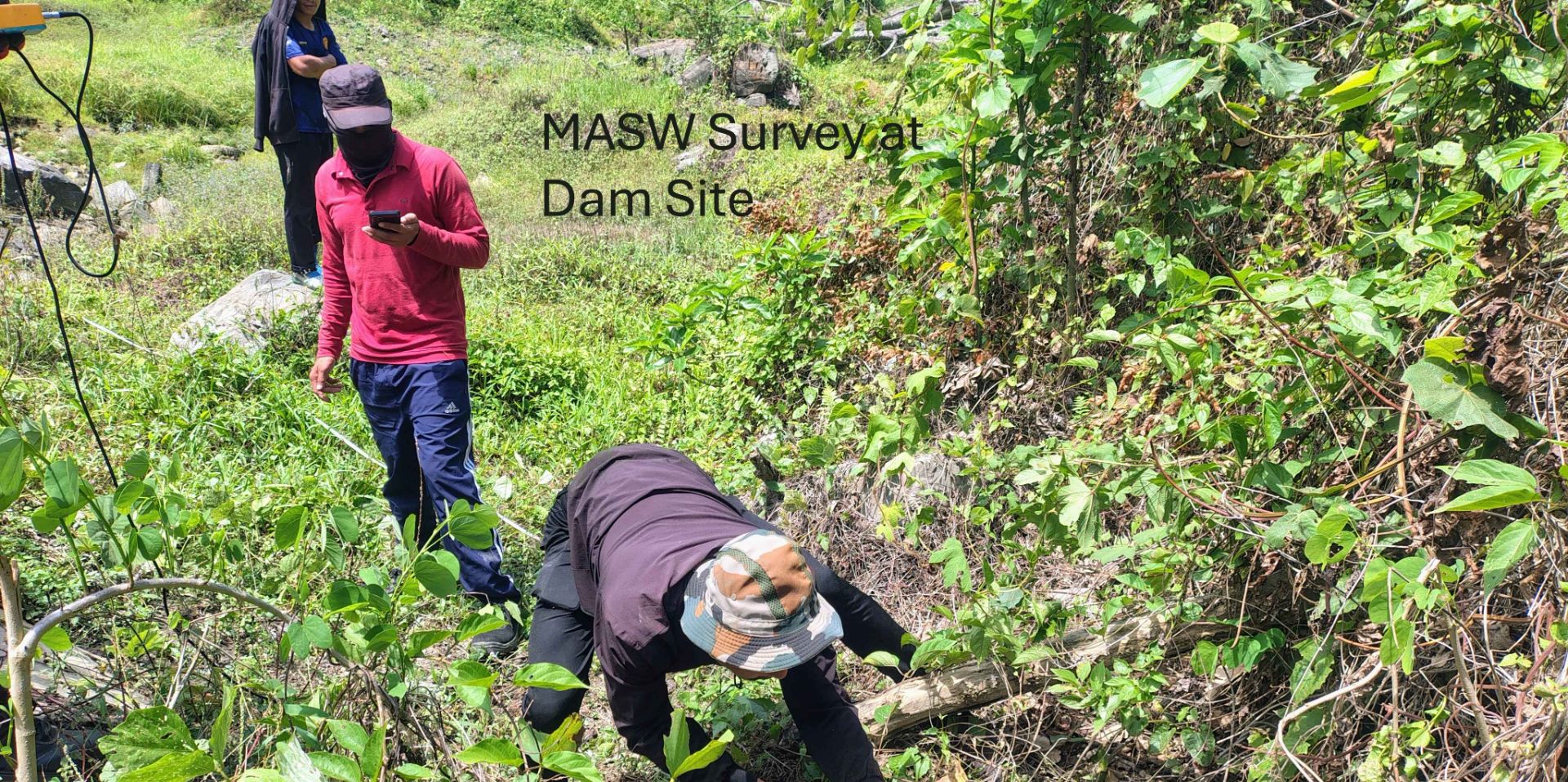
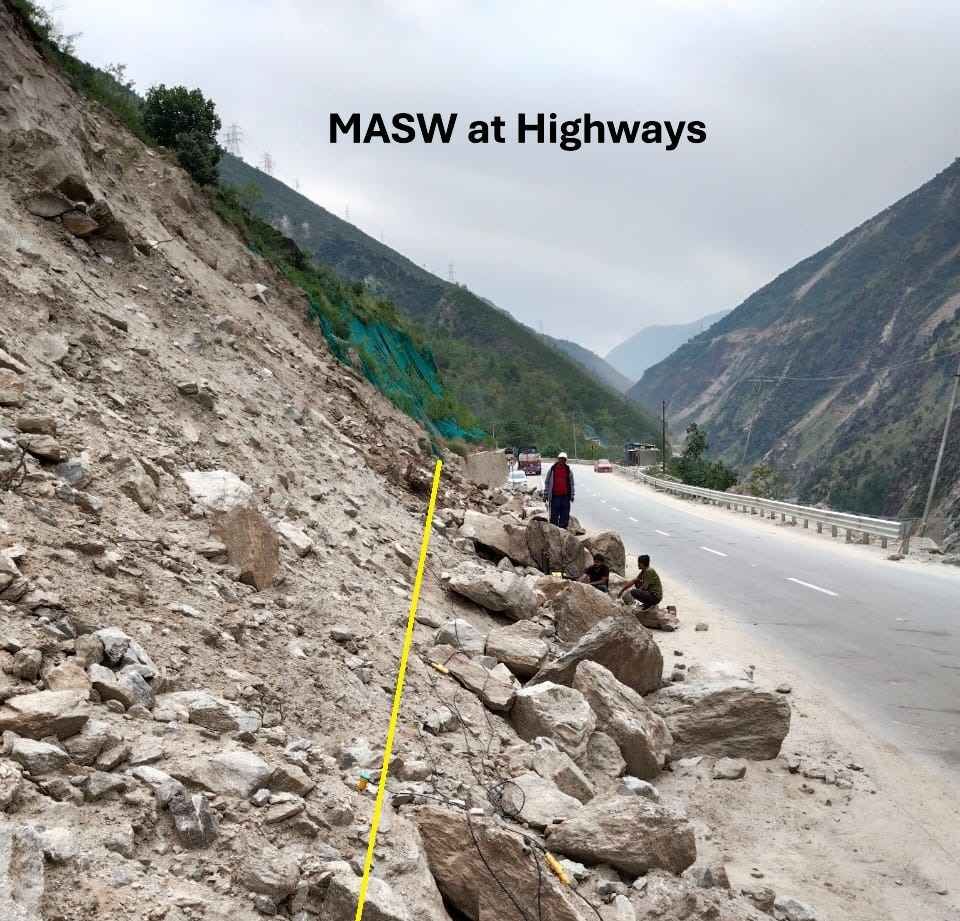
- Dam, Tunnel and infrastructure projects investigations
- Monitoring compaction
- Archaeological surveys